Associated Learning Outcome:
At the end of this module, learners will be able to:
- Learners will be able to identify the pros and cons of using steel beams as the primary structural building material in a new construction project.
- Learners will be able to identify the sources of greenhouse gas emissions associated with steel beams.
Introduction to Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron, carbon, and a small percentage of other metals such as nickel, chromium, aluminum, and cobalt [7]. Structural steel most commonly comes in three different shapes (but not limited to): I-beam, L-beam, and T-beam. These shapes utilize different properties such as cross-sectional area, the moment of inertia, and density to achieve different strength properties tailored to their use.
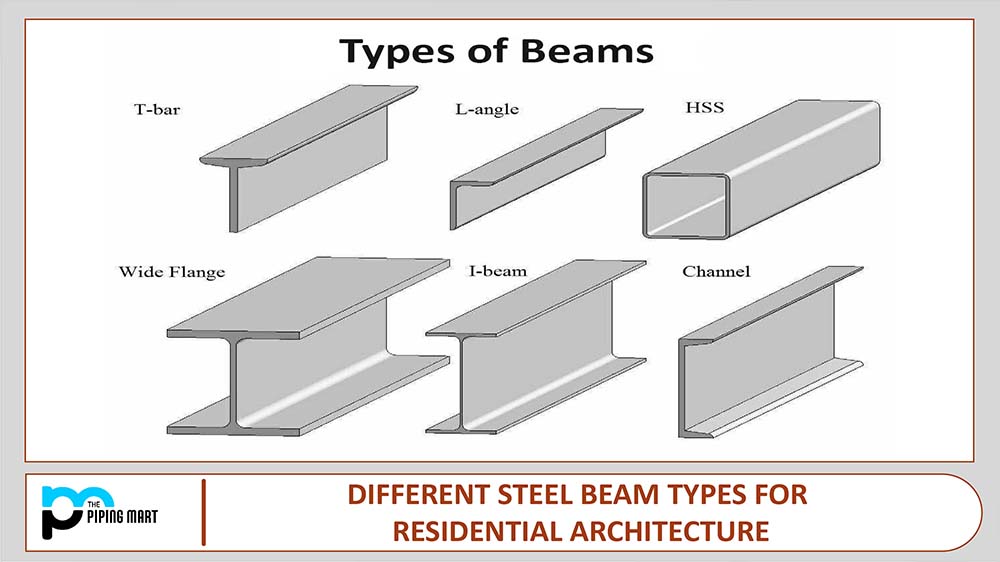
These shapes are typically achieved by processes such as hot rolling or cold rolling. See here for an overview of the differences between hot rolling and cold rolling (required).
The steel beams are constructed into a steel frame, often referred to as the “skeleton frame” of a building and support the walls, floors, and roof. The skyscraper is only possible because of this method.

Various codes dictate the standard sizing required of beams. These tables are available at sources like SkyCiv below.
Test your Understanding!
Advantages of Steel Beams
As a structural material, steel beams hold many benefits to them. The main advantage of using steel is its strength. Steel is known for being highly durable and resistant to damage caused by natural disasters such as earthquakes and hurricanes [8].
As discussed, steel beams are made by hot rolling or cold rolling. this process allows the beams to be highly customizable to fit the strength and size requirements calculated by the design engineer. Additionally, architects are able to utilize the versatility of steel to unlock their creativity.
- Structural steel is resistant to fire (if fabricated to be), wind and earthquakes
- Structural steel is easy to work with and can be cut, drilled, or welded as needed for the project, allowing for a high customization ability
- Structural steel is one of the most versatile building materials available
Disadvantages of Steel Beams
While structural steel beams come with many benefits, they also come with many downfalls. Manufacturers of steel beams require specialized knowledge and machinery which leads to a higher price tag upon purchase, typically higher than concrete or timber. Additional costs come from the transportation of the steel. Steel weighs more than concrete and timber which makes transportation and installation more difficult.
An additional disadvantage to steel is the maintenance required. Steel is susceptible to rust and corrosion which then requires regular inspections and repair to prevent structural damage.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Structural Steel
The greenhouse gas emissions associated with structural steel beams can vary depending on several factors, including the production process, transportation, and the source of the energy used. The primary greenhouse gas emitted during the production of structural steel is carbon dioxide (CO2).
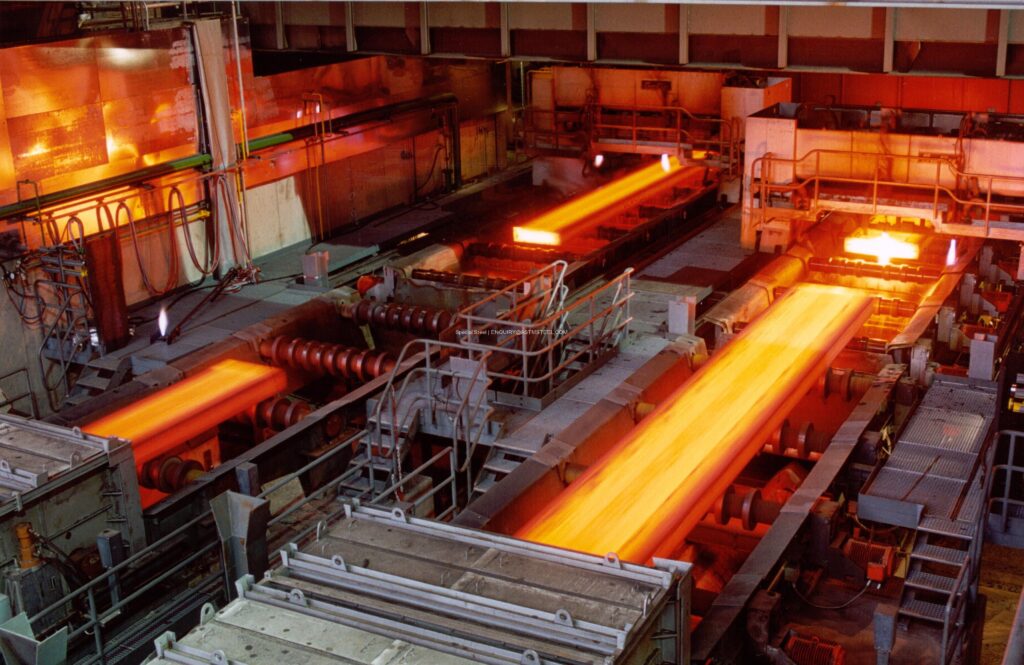

The production of structural steel involves extracting iron ore, which is then processed in a blast furnace to produce iron. The iron is then combined with other elements, such as carbon, to create steel. The carbon used in this process comes from a variety of sources, including coal and natural gas. The combustion of these carbon sources releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
Additionally, the energy required for heating and shaping the steel, as well as transportation to the construction site, can also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The source of energy used during these processes determines the emissions associated with these activities. If the energy is derived from fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, it will result in higher emissions compared to renewable energy sources [9].
(Required) Review the carbon footprint of steel and compare the carbon footprint of different projects here
(Optional) Use SAP2000 to analyze the strengths of different steel types. This is not a course requirement, however, participating can greatly increase your understanding of how different shapes of steel behave. Create a truss or square frame with varying dead and live loads and compare the deflected shapes using different material properties. If you haven’t used SAP2000, click here for an extensive library of tutorials.